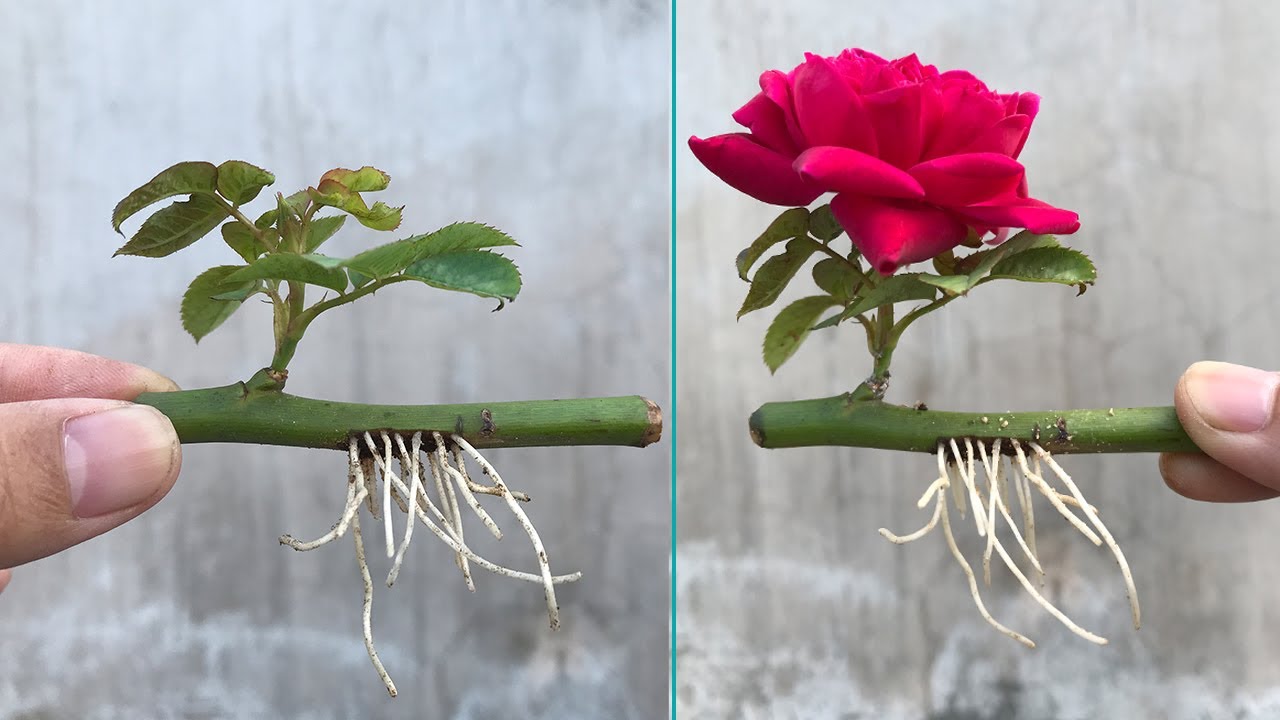
How To Propagate Roses From Cuttings: Your Path to a Vibrant, Blooming Garden – Propagate Roses From Cuttings: Your Path to a Vibrant, Blooming Garden – Roses, with their captivating beauty and timeless symbolism, have long been a cherished addition to gardens worldwide. Their vibrant blooms and intoxicating fragrance evoke feelings of joy and romance, making them a popular choice for landscaping and floral arrangements.
But beyond their aesthetic appeal, roses offer a unique opportunity for gardeners to experience the rewarding process of propagation. Growing roses from cuttings is a cost-effective and fulfilling way to expand your rose collection and create a vibrant, blooming garden.
This comprehensive guide will lead you through the steps of successfully propagating roses from cuttings, from selecting the right stems to nurturing them into healthy, thriving rose bushes. We’ll explore various rooting methods, provide essential care tips, and address common challenges you might encounter along the way.
Whether you’re a seasoned gardener or a curious beginner, this guide will equip you with the knowledge and confidence to embark on your own rose propagation journey.
Introduction
Roses, with their captivating beauty and intoxicating fragrance, have captivated hearts and adorned gardens for centuries. They are a symbol of love, passion, and elegance, making them a cherished addition to any landscape. Beyond their aesthetic appeal, roses possess a rich cultural and historical significance, interwoven with mythology, poetry, and art.The allure of roses extends beyond their visual charm.
They offer a multitude of benefits for gardeners and enthusiasts alike. Roses provide a vibrant burst of color and fragrance, attracting pollinators and creating a welcoming atmosphere. They can be grown in various forms, from classic bushes to climbing varieties, allowing for creative landscaping and design possibilities.
The Advantages of Propagating Roses from Cuttings
Propagating roses from cuttings is a rewarding and cost-effective method for expanding your rose collection. This technique allows you to create new plants from existing roses, preserving their unique characteristics and ensuring genetic continuity. By taking cuttings from your favorite roses, you can enjoy their beauty and fragrance throughout your garden, while also sharing them with friends and family.
Choosing the Right Cuttings
The success of your rose propagation journey hinges on selecting the right cuttings. Choosing healthy, disease-free stems at the ideal time of year maximizes your chances of rooting success.
Timing for Rose Cuttings
The optimal time to take rose cuttings is during the growing season, when the plant is actively producing new growth. This period typically falls between late spring and early summer, when temperatures are warm and the plant is actively producing new growth.
- Spring:The best time for taking cuttings is in the spring, after the last frost has passed and new growth has emerged. This period allows the cuttings to develop a strong root system before the onset of winter.
- Early Summer:Taking cuttings in early summer, when the plant is actively growing, also yields good results. However, avoid taking cuttings during the hottest months of summer, as the heat can stress the plant and hinder root development.
- Late Summer:While less ideal than spring or early summer, you can still take cuttings in late summer. However, the success rate may be lower due to shorter days and cooler temperatures. It is crucial to provide adequate protection for the cuttings during the winter months.
Characteristics of Healthy Rose Stems
The ideal rose stem for propagation should exhibit certain characteristics that indicate its health and vigor.
- Mature Wood:Choose stems that have matured, but are still pliable and not too woody. Avoid using very young, green stems or overly mature, hard stems, as they may be difficult to root.
- Healthy Growth:Select stems that are free from disease, pests, and damage. Look for stems that are vigorous and have a healthy, vibrant color. Avoid using stems with signs of discoloration, spots, or other abnormalities.
- Current Season’s Growth:It is recommended to select cuttings from the current season’s growth, as this wood is generally more receptive to rooting. Avoid using stems from the previous year’s growth, as they are more likely to be woody and less responsive to propagation.
Disease-Free Plants
Selecting cuttings from disease-free plants is crucial for successful propagation and preventing the spread of diseases to your garden.
- Visual Inspection:Carefully inspect the rose plant for any signs of disease, such as leaf spots, powdery mildew, or rust. Avoid taking cuttings from plants that show any signs of infection.
- Healthy Root System:A healthy rose plant will have a well-developed root system, indicating its overall health and vigor. A healthy root system is essential for the successful propagation of cuttings.
- Proper Care:Providing proper care to your rose plants, such as adequate watering, fertilization, and pest control, can help prevent diseases and ensure the health of your plants. This, in turn, will increase the success rate of propagation.
Preparing the Cuttings
Preparing your rose cuttings correctly is crucial for their successful rooting. The right preparation ensures the cuttings have the best chance of developing strong roots and thriving in their new environment.
Cutting Angles and Length
The angle at which you cut your rose cuttings and the length of the cutting play a significant role in their ability to root.
- Cuttings should be taken from healthy, disease-free stems that are actively growing.
- Use a sharp, clean knife or pruning shears to make a clean cut at a 45-degree angle just below a node. This angle provides a larger surface area for root development.
- The ideal length for rose cuttings is 4-6 inches. This length provides enough stem for root development and allows for sufficient leaves to perform photosynthesis.
Removing Leaves from the Lower Portion
Removing leaves from the lower portion of the cutting is essential for promoting root growth.
- Leaves below the soil line will rot and can introduce disease to the cutting.
- Remove all leaves from the bottom 2-3 inches of the cutting.
- You can also pinch off some of the top leaves to reduce water loss and focus energy on root development.
Using Sharp, Clean Tools
Using sharp, clean tools is essential for preventing disease and ensuring a clean cut.
- Dull tools can crush the stem and create an entry point for bacteria and fungi.
- Clean your tools with rubbing alcohol or a bleach solution before and after each use to prevent the spread of disease.
Rooting Methods: How To Propagate Roses From Cuttings: Your Path To A Vibrant, Blooming Garden

The success of rose propagation hinges on the establishment of a robust root system. There are various methods to encourage root development, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. Understanding these techniques will enable you to choose the most suitable method for your needs.
Water Propagation
Water propagation offers a simple and accessible method for rooting rose cuttings. It allows for easy observation of root development and minimizes the risk of fungal infections common in soil-based methods. However, it’s less efficient than soil propagation, as roots may be more delicate and less adapted to soil conditions.
Step-by-Step Guide for Water Propagation
- Prepare a clean glass jar or vase, ensuring it’s free of any residues that could harm the cutting.
- Fill the jar with fresh, clean water, reaching about an inch below the top. You can add a tablet of rooting hormone to the water to encourage root growth.
- Place the prepared cutting into the jar, ensuring the nodes (points where leaves emerge) are submerged in the water.
- Position the jar in a bright location, avoiding direct sunlight, which can overheat the water.
- Change the water every few days to prevent the growth of bacteria and algae.
- Once roots have developed, usually within 2-4 weeks, transplant the cutting into a pot filled with a well-draining potting mix.
Soil Propagation
Soil propagation is the most common and generally successful method for rooting rose cuttings. It provides a stable environment for root development and encourages the formation of strong, sturdy roots. However, it requires more attention and care, as it involves maintaining the appropriate soil moisture levels and protecting the cuttings from pests and diseases.
Step-by-Step Guide for Soil Propagation
- Select a pot with drainage holes and fill it with a well-draining potting mix, such as a blend of peat moss, perlite, and vermiculite.
- Moisten the potting mix thoroughly, ensuring it’s evenly damp but not waterlogged.
- Dip the cut end of the prepared cutting in rooting hormone powder, ensuring the hormone coats the entire cut surface.
- Make a small hole in the potting mix using a pencil or your finger. Insert the cutting into the hole, ensuring the nodes are buried beneath the soil.
- Firm the soil around the cutting gently to provide stability.
- Water the cutting lightly, ensuring the soil is moist but not soggy.
- Cover the pot with a clear plastic dome or bag to create a humid environment that promotes root development.
- Place the pot in a bright location, avoiding direct sunlight.
- Monitor the soil moisture regularly, watering as needed to keep it consistently moist.
- Remove the plastic dome or bag after several weeks when new growth appears, indicating successful rooting.
Using Rooting Hormone
Rooting hormone is a synthetic or natural compound that promotes root development in plant cuttings. It contains auxins, plant hormones that stimulate cell division and root formation. Using rooting hormone can significantly increase the success rate of rose propagation, especially for difficult-to-root varieties.
Advantages of Using Rooting Hormone
- Increased Rooting Success:Rooting hormone accelerates root development, leading to a higher percentage of cuttings successfully rooting.
- Faster Root Growth:Rooting hormone promotes rapid root formation, allowing the cuttings to establish themselves quickly.
- Improved Root Structure:Rooting hormone encourages the development of a strong and extensive root system, making the plant more resilient and vigorous.
Disadvantages of Using Rooting Hormone
- Potential for Overuse:Excessive use of rooting hormone can lead to stunted growth or root damage.
- Cost:Rooting hormone can be an additional expense, especially for large-scale propagation.
- Environmental Concerns:Some synthetic rooting hormones may have environmental impacts.
Types of Rooting Hormone
- Powdered Rooting Hormone:This is the most common type, readily available at garden centers. It’s easy to apply by dipping the cut end of the cutting in the powder.
- Liquid Rooting Hormone:This type is typically diluted in water and applied to the cutting using a spray bottle or by soaking the cutting in the solution.
- Gel Rooting Hormone:This type is a gel-like substance that adheres to the cutting, providing a continuous release of rooting hormone.
Maintaining the Cuttings
After you’ve successfully rooted your rose cuttings, the next crucial step is to maintain them properly to ensure they thrive and develop into healthy, vibrant plants. Providing adequate moisture, light, and protection from pests and diseases are essential for their growth and survival.
Moisture and Light
Maintaining the right moisture levels is critical for the cuttings’ development. Newly rooted cuttings require consistent moisture to support their growth, especially during the initial stages. However, overwatering can lead to root rot, so it’s essential to strike a balance.
- Regular Watering:Check the soil moisture regularly and water when the top inch of soil feels dry. Avoid letting the soil completely dry out, as this can stress the cuttings.
- Drainage:Ensure that the container has adequate drainage to prevent waterlogging. Excess water should be able to drain freely, preventing root rot.
- Light:Rose cuttings need bright, indirect light to photosynthesize and grow. Place them in a location that receives several hours of sunlight daily, but avoid direct sunlight, especially during the hottest part of the day, which can scorch the leaves.
Temperature and Humidity
Optimal temperatures and humidity levels are crucial for successful rooting.
- Temperature:Warm temperatures, between 65-75°F (18-24°C), are ideal for rooting. You can use a heating mat to maintain a consistent temperature, especially during cooler months.
- Humidity:High humidity levels, around 70-80%, are beneficial for cuttings, as they help prevent dehydration. You can create a humid environment by placing the cuttings in a humidity dome or by misting them regularly.
Pest and Disease Protection
Rose cuttings can be susceptible to pests and diseases, which can hinder their growth and even kill them.
- Regular Inspection:Inspect the cuttings regularly for any signs of pests or diseases, such as aphids, spider mites, powdery mildew, or black spot.
- Treatment:If you detect any pests or diseases, treat them promptly with appropriate insecticides or fungicides. Choose organic options whenever possible.
- Prevention:Maintaining good hygiene practices, such as cleaning tools and pots before use, can help prevent the spread of pests and diseases.
Transplanting the Rooted Cuttings
After weeks of patiently nurturing your rose cuttings, the time has come to transplant them into their permanent homes. This step marks a significant milestone in your rose propagation journey, and it’s crucial to execute it with care to ensure the young plants thrive.
Transplanting into Individual Pots, How To Propagate Roses From Cuttings: Your Path to a Vibrant, Blooming Garden
Once the cuttings have developed a robust root system, they are ready for transplanting. This method is ideal for further nurturing the plants before introducing them to the garden environment.
- Choose the Right Pot:Select pots that are slightly larger than the root ball of the cuttings. A pot size of 1-2 gallons is generally suitable. Ensure the pots have drainage holes to prevent waterlogging.
- Prepare the Potting Mix:Use a well-draining potting mix specifically formulated for roses. You can also add a small amount of compost or aged manure to enrich the soil.
- Gently Remove the Cutting:Carefully remove the cutting from its rooting container, taking care not to disturb the roots. If the cutting is stuck, you can gently tap the bottom of the container to loosen it.
- Plant the Cutting:Place the cutting in the center of the new pot, ensuring the root ball is level with the soil surface. Fill the pot with potting mix, leaving about an inch of space at the top.
- Water Thoroughly:After planting, water the cutting generously to settle the soil and provide moisture to the roots.
Transplanting Directly into the Garden
For those eager to see their roses blooming in the garden, direct planting is an option. However, it’s essential to ensure the cuttings are well-established and the garden environment is suitable.
- Choose the Right Location:Select a sunny spot in your garden that receives at least 6 hours of direct sunlight daily. Roses prefer well-drained soil with a pH between 6.0 and 7.0.
- Prepare the Soil:Dig a hole twice the width and depth of the root ball. Amend the soil with compost or aged manure to improve drainage and nutrient content.
- Plant the Cutting:Place the cutting in the hole, ensuring the root ball is level with the soil surface. Backfill the hole with the amended soil, gently pressing it down around the roots.
- Water Thoroughly:After planting, water the cutting deeply to settle the soil and provide moisture to the roots.
Hardening Off the Plants
Before transplanting your rose cuttings into their permanent homes, it’s crucial to harden them off. This process gradually acclimates the plants to the outdoor environment, reducing the risk of shock and ensuring a successful transition.
Cultivating a vibrant rose garden doesn’t have to break the bank. Propagating roses from cuttings is a rewarding and cost-effective way to expand your collection. To truly unlock the secrets to a stunning rose garden, delve into the intricacies of rose propagation with our comprehensive guide, How To Propagate Roses From Cuttings: Unveil the Secrets to a Stunning Rose Garden.
Armed with the right techniques, you’ll be well on your way to a blooming oasis of fragrant roses.
- Start Gradually:Begin by placing the cuttings in a sheltered location outdoors for a few hours each day, increasing the exposure time gradually over several days.
- Choose a Protected Spot:Select a spot that is sheltered from strong winds and harsh sunlight. A shaded area or under a tree canopy is ideal.
- Monitor the Plants:Observe the plants closely for any signs of stress, such as wilting or leaf drop. If you notice any signs of stress, reduce the exposure time or move the plants to a more sheltered location.
Caring for Newly Transplanted Rose Bushes
After transplanting, providing consistent care is essential to help the young rose bushes establish themselves.
- Water Regularly:Water the newly transplanted rose bushes deeply and regularly, especially during dry periods. The soil should be consistently moist but not waterlogged.
- Fertilize Regularly:Apply a balanced rose fertilizer every 4-6 weeks to provide the necessary nutrients for growth and flowering. Avoid over-fertilizing, as it can damage the roots.
- Prune Regularly:Pinch off any flower buds that appear in the first year after transplanting. This encourages the plant to focus its energy on root development and establish a strong foundation.
- Protect from Pests and Diseases:Regularly inspect the rose bushes for signs of pests or diseases. Treat any problems promptly to prevent them from spreading.
Growing Healthy Rose Bushes
Once your rose cuttings have successfully rooted, nurturing them into thriving rose bushes requires consistent care and attention. Understanding the essential requirements for rose growth will ensure your new plants flourish and reward you with beautiful blooms.
Rose Bush Care Requirements
A well-structured care routine is essential for the health and vitality of your rose bushes. The table below Artikels the key factors that contribute to their optimal growth and flowering:
Requirement |
Description |
Illustration |
|---|---|---|
Sunlight |
Rose bushes thrive in full sun, receiving at least 6 hours of direct sunlight daily. This promotes healthy growth and abundant blooms. |
A depiction of a rose bush basking in the warm rays of the sun. The image could show the plant with lush green foliage and vibrant blooms, showcasing the positive impact of sunlight on its growth. |
Watering |
Water your rose bushes deeply but infrequently, allowing the soil to dry slightly between waterings. Avoid overwatering, which can lead to root rot. |
A visual representation of a gardener gently watering a rose bush with a watering can. The image should depict the water reaching the roots of the plant, emphasizing the importance of deep watering. |
Fertilization |
Regular fertilization is crucial for providing essential nutrients to your rose bushes. Use a balanced fertilizer specifically formulated for roses, applying it according to the manufacturer’s instructions. |
An illustration of a rose bush with a bag of fertilizer nearby. The image could show the fertilizer being applied to the soil around the base of the plant, highlighting the importance of providing nutrients for healthy growth. |
Pruning |
Regular pruning helps to maintain the shape and health of your rose bushes. Remove dead or diseased branches, as well as any stems that are crossing or growing inward. |
A visual representation of a gardener pruning a rose bush with hand pruners. The image should depict the removal of dead or diseased branches, emphasizing the importance of proper pruning techniques for healthy growth. |
Troubleshooting Common Problems
Even with careful propagation techniques, challenges can arise during the process. Recognizing and addressing these issues promptly can increase your success rate and ensure healthy rose bushes. This section will guide you through common problems, their causes, and effective solutions.
Wilting
Wilting is a common issue, often indicating insufficient water absorption. This can be caused by various factors, including:
- Insufficient watering:Ensuring consistent moisture is crucial. Check the soil moisture regularly and water thoroughly when the top inch of soil feels dry. Avoid overwatering, as it can lead to root rot.
- Root damage:During handling or transplanting, delicate roots can be damaged, hindering water uptake. Be gentle with the cuttings and minimize disturbance to the roots.
- High temperatures:Excessive heat can lead to dehydration and wilting. Ensure the cuttings are protected from direct sunlight and placed in a shaded area with good air circulation.
- Improper rooting medium:A well-draining, moisture-retentive medium is essential for healthy root development. Use a mixture of peat moss, perlite, and vermiculite, or a commercial rooting mix.
To address wilting, first, assess the cause. If insufficient watering is the culprit, water thoroughly and monitor the cuttings for improvement. If root damage is suspected, gently check for any broken or damaged roots and prune them if necessary. Provide shade and increase humidity if high temperatures are the issue.
Lastly, consider repotting the cuttings into a suitable rooting medium if the current one is inadequate.
Root Rot
Root rot is a serious fungal disease that can occur when the roots are constantly exposed to excessive moisture. Symptoms include wilting, yellowing leaves, and a foul odor from the soil.
- Overwatering:Excessive watering creates a waterlogged environment, making it difficult for roots to breathe. Ensure proper drainage and allow the soil to dry slightly between waterings.
- Poor drainage:A poorly draining potting mix or container can trap water, leading to root rot. Use a well-draining mix and ensure the container has drainage holes.
- Infected rooting medium:Using a contaminated rooting medium can introduce fungal spores that cause root rot. Sterilize the rooting medium before use.
To prevent root rot, use a well-draining rooting medium, water sparingly, and ensure proper drainage. If root rot is detected, remove the cuttings from the infected medium, trim away any damaged roots, and repot them in fresh, sterilized soil. You can also treat the soil with a fungicide to control the fungal infection.
Pest Infestations
Rose cuttings are susceptible to various pests, including aphids, spider mites, and whiteflies. These pests can damage the leaves, stems, and buds, hindering the growth of the cuttings.
- Aphids:These small, soft-bodied insects feed on plant sap, causing leaves to curl and distort. They also secrete a sticky substance called honeydew, which attracts ants and can lead to fungal growth.
- Spider mites:These tiny, spider-like creatures create fine webs on the underside of leaves and suck sap, causing yellowing and browning of leaves.
- Whiteflies:These small, white, flying insects lay their eggs on the underside of leaves. The larvae feed on plant sap, causing leaf yellowing and wilting.
To prevent pest infestations, inspect the cuttings regularly for signs of infestation. Use insecticidal soap or neem oil to control pests. You can also introduce beneficial insects like ladybugs, which prey on aphids and other pests.
Common Rose Diseases
Disease |
Symptoms |
Treatment |
|---|---|---|
Black Spot |
Black, circular spots on leaves, often with yellow halos |
Remove infected leaves, improve air circulation, use fungicides |
Powdery Mildew |
White, powdery coating on leaves and stems |
Remove infected leaves, improve air circulation, use fungicides |
Rust |
Orange or brown pustules on the underside of leaves |
Remove infected leaves, improve air circulation, use fungicides |
Rose Mosaic Virus |
Yellowing, mottling, and distortion of leaves |
No cure, remove infected plants to prevent spread |
Conclusion
Propagating roses from cuttings is a rewarding and accessible way to expand your rose garden, enjoy the beauty of these flowers, and share your passion with others. By following the steps Artikeld in this guide, you can confidently embark on your own rose propagation journey.
The Rewards of Propagating Roses
The journey of propagating roses from cuttings is filled with satisfaction and joy. Witnessing a tiny cutting transform into a thriving rose bush is a testament to your dedication and patience. You’ll gain a deeper appreciation for the resilience and beauty of these remarkable plants.
Propagating roses from cuttings is a rewarding and cost-effective way to expand your rose garden. This technique allows you to create new plants from existing ones, offering a wide variety of roses without breaking the bank. To learn more about the benefits of propagating roses from cuttings and discover how to quickly achieve a beautiful rose garden, check out our comprehensive guide, From Cuttings to Roses: How To Achieve a Beautiful Rose Garden Quickly.
By mastering this simple technique, you can enjoy a vibrant, blooming garden filled with your favorite roses.
- Sharing the Joy:You can share your propagated roses with friends, family, and fellow gardening enthusiasts, spreading the beauty and joy of these flowers.
- Cost-Effective Gardening:Propagating roses from cuttings is a cost-effective way to expand your rose garden without breaking the bank. You can create multiple new plants from a single rose bush.
- Unique and Diverse Garden:Propagating roses from cuttings allows you to cultivate a diverse collection of roses, including rare varieties and heirloom cultivars.
Ultimate Conclusion
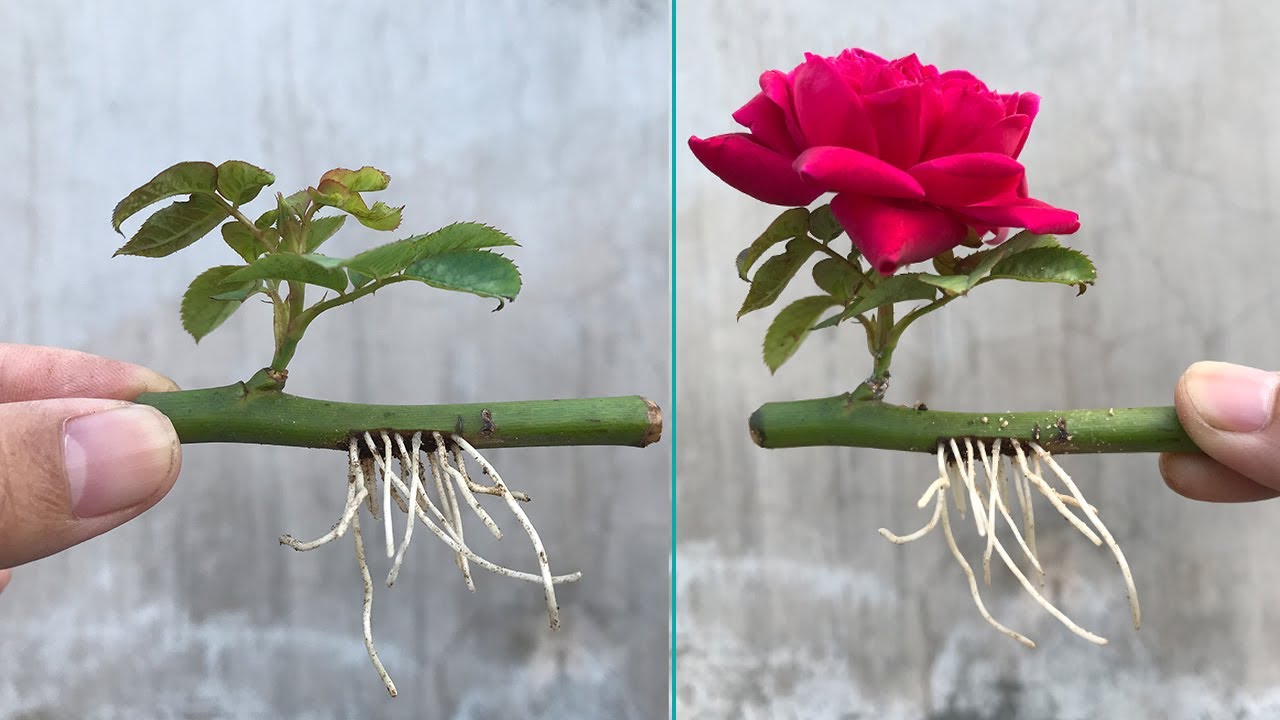
Propagating roses from cuttings is a rewarding experience that allows you to share the beauty of these beloved flowers with your garden and beyond. By following the steps Artikeld in this guide, you can successfully cultivate healthy rose bushes from cuttings, creating a vibrant and fragrant oasis that will bring joy for years to come.
So, gather your tools, select your favorite rose varieties, and embrace the fulfilling journey of propagating roses from cuttings.
Clarifying Questions
What is the best time of year to take rose cuttings?
The ideal time to take rose cuttings is during the dormant season, typically in late fall or early winter, before the plant begins to actively grow. This is when the rose is storing energy in its roots, making it easier for the cuttings to develop roots.
How do I know if a rose cutting is rooted?
You can check for roots by gently tugging on the cutting. If it feels firm and doesn’t come out easily, it has likely developed roots. You can also look for new growth at the base of the cutting, indicating that the roots are absorbing water and nutrients.
What are some common problems I might encounter when propagating roses from cuttings?
Common problems include wilting, root rot, and pest infestations. Wilting can be caused by insufficient watering or excessive heat. Root rot can occur if the cuttings are kept in overly moist conditions. Pest infestations can be prevented by keeping the cuttings clean and free of debris.